ChirpStack V4 Connector
Connector details ChirpStack
The ChirpStack V4 connector allows the platform to provision devices and subscribe to device updates from a ChirpStack V4 LoRaWAN server. This automates the ChirpStack integration, enabling full device management directly within Yggio. Supported operations include:
- Provisioning new devices
- Subscribing to device updates
- Deleting devices
Requirement: MQTT broker added to ChirpStack v3, such as Mosquitto.
Required Information
To set up a connection to a ChirpStack v4 server, provide the following:
- a. ChirpStack API and MQTT broker URL: lora.yggio.net (Sensative ChirpStack V4 LoraWAN server)
- b. Tenant UUID: The Tenant UUID to use in ChirpStack
- c. Token: An API key generated in the Tenant
- d. MQTT Username: Your MQTT username
- e. MQTT Password: Your MQTT password
- f. Application UUID: The application UUID to use in ChirpStack
Extra information
- Default Flow: Which defaulf flow should be used for IoT nodes using the connector
- Retention Policy: Which default retention policy should be used for IoT nodes using the connector
⚠️ ChirpStack V4 must be preconfigured with all of the details listed above, and the API user must be active and have an Admin role to perform these operations. If you receive a 40x error response, it's likely due to wrong UUIDs, wrog API key, wrong credentials, wrong URL or insufficient access rights. Alternatively the credential configuration files in ChirpStack or the MQTT broker are not accurate. Make sure all the configuration and settings are reviewed and adjusted accordingly.
Configure ChirpStack
Start With Setting Up the Access
Log in to your ChirpStack server and create an API user account. If needed, also create a new Tenant and Application. If you don’t have your own LoRaWAN server but want a private setup, please reach out to your support contact.
- a. The account must be linked to both an Tenant and an Application to enable device provisioning.
- b. The user must have the role
Adminin the Tenant - c. In the Tenant create an API key, this key will only be visible once and must be entered into the Connector in the IoT platform. Make sure you copy it.
Note that ID for Tenant and Application is available in the browser URL
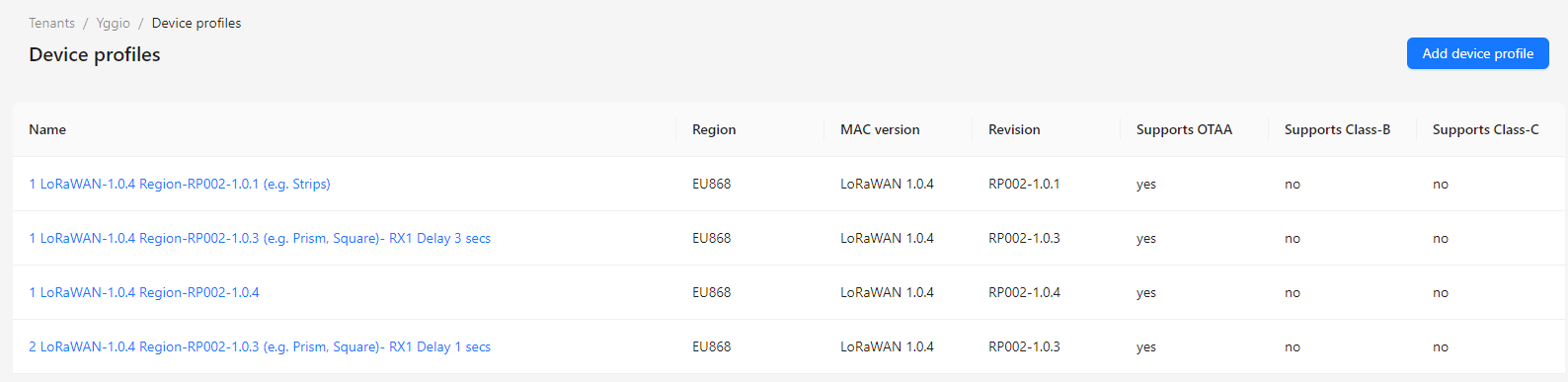
Create Device Profiles
In ChirpStack, you need to create Device Profiles. These define the LoRaWAN settings to use, including whether OTAA is supported, the LoRaWAN version (commonly 1.0.2, 1.0.4, or 1.1), Regional Parameters (e.g., Region A, B, or a specific RP version), and whether the device uses Class A or Class C. Additional parameters may also apply.
Device Profiles are important—if the settings don't match the actual device, LoRaWAN messages may be lost, and actuators won't respond instantly unless Class C is enabled.
Once configured, the Device Profiles will appear in the IoT platform when creating a new LoRaWAN device.
Setting Up the Connector
Once the ChirpStack configuration is complete, proceed to the IoT plattform:
- Navigate to Connectors → New Connector → ChirpStack V4 Connector
- Fill in the required fields with the collected information.
Note that the Network Server ID, Tenant ID, and Application ID can all be found in your browser’s URL bar. Below is an example for the Network Server, and the images above provide further detail.
Verifying the Connector
-
The platform will automatically verify the connection when the connector is created,
but this does not guarantee full functionality. -
To perform a full verification:
- Create a device in the platform using the ChirpStack connector.
- After creation, open the device page.
- Go to Tools and check the Synchronize status — it should not say
"never". - Click the Synchronize button manually to confirm it works successfully.
- Log in to ChirpStack and confirm that the device has been provisioned.
- Trigger (or wait for) the device’s first uplink.
- Ensure that the uplink is received and properly decoded by the platform.
Multi-Account Setup
There are two main ways to integrate ChirpStack with the IoT platform:
1. Users need access to ChirpStack
Mirror parts of the IoT platform's organization structure in the ChirpStack server. Users can be given ChirpStack accounts to view LoRaWAN-specific connection parameters and create new Device Profiles.
In this setup, create one connector per tenant.
2. Users do not need access to ChirpStack
Use a flat structure in ChirpStack, where all devices are managed in a single shared location.
Only one connector is required in the IoT platform and can be shared with all users who need to add devices.
Note: ChirpStack V4 does not support billing, so billing must be handled through the IoT platform.
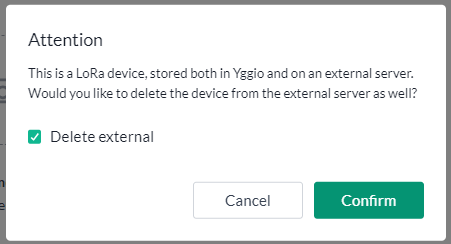
⚠️ Important:
If a device is deleted from the IoT plattform, it will by default also be deleted and decommissioned from the ChirpStack LoRaWAN server. To avoid this, make sure to opt out of the delete action when prompted during the confirmation dialog.
Gateway Config
With ChirpStack v4 it is recommended to use LoRa Basics Station instead of the legacy UDP packet forwarder. This is a table comparing the two gateway connectivity options.
| Feature | LoRa Basics™ Station | Legacy UDP Packet Forwarder |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Protocol | Secured IP connection (WebSockets/TCP) | Connectionless UDP |
| Security | State-of-the-art TLS and token-based authentication | No transport-level security or authentication. However, LoRaWAN payloads remain encrypted end-to-end |
| Reliability | More reliable due to TCP handling, retries, and acknowledgement of packets | "Fire and forget", packets can be lost in transit without notification |
| Timekeeping | No dependency on local gateway timekeeping | Requires accurate local time synchronization for proper operation |
| Scalability | Designed for robust, large-scale, commercial network deployments | Suitable for smaller or simpler deployments |
| Bandwidth Usage | Uses JSON protocol, which may use slightly more bandwidth than binary | Simple, generally lower data usage |
| Industry Support | Becoming the new industry standard and preferred by major network servers | Legacy support is being phased out by many network and gateway providers |
| Ease of Use | Requires managing security keys and certificates, adding complexity | Simple to set up and generally well understood, no TLS certificate handling needed |
| Management | Centralized update and configuration management for gateway fleets (CUPS protocol) | No remote management, configuration must be done locally |
In summary, LoRa Basics™ Station offers a more modern, secure, and reliable solution compared to legacy UDP packet forwarders. However, managing TLS certificates and their expiry dates can be challenging, especially without a CUPS server or other centralized gateway management system. Proper planning and proactive certificate management are essential to ensure smooth operation.
Troubleshooting
I get a 40x error
- This typically indicates an issue with your URL, credentials, or access rights. Eliminate these one at a time:
- Double-check the URL—make sure there’s no trailing
/at the end. - Verify that the username, password, and access permissions are correct.
- Double-check the URL—make sure there’s no trailing
I get no uplink in the IoT platform
- Go to the sensor in the ChirpStack user interface.
- Confirm that the device actually has sent uplinks.
- Confirm that the MQTT URL and credentials in the connection is accurate and that no trailing
/at the end - If it is your own new ChirpStack, confirm that on the MQTT broker log that it can authenticate and authorize to ChirpStack bu subscribing with a local broker. If it fails edit your MQTT authorization files in ChirpStack.
I have an API Gateway between me and ChirpStack — what should I do?
- Ensure the API gateway gives access to both the ChirpStack API and the ChirpStack MQTT broker.
- When creating the connector, update the API and MQTT URLs to point to the gateway endpoints that route correctly to ChirpStack.
I get a 40x error when trying to import or create devices — what could be the issue?
- A 40x error means ChirpStack is rejecting the request. This is usually caused by:
- Incorrect credentials
- Wrong URL
- Missing or incorrect access rights on the ChirpStack side
- Go through the example setup images and verify the following:
- Username, password, API URL
- Network Server ID, Tenant ID and Application ID
- Also confirm:
- The ChirpStack API user account is marked as an Admin User in the correct Tenant